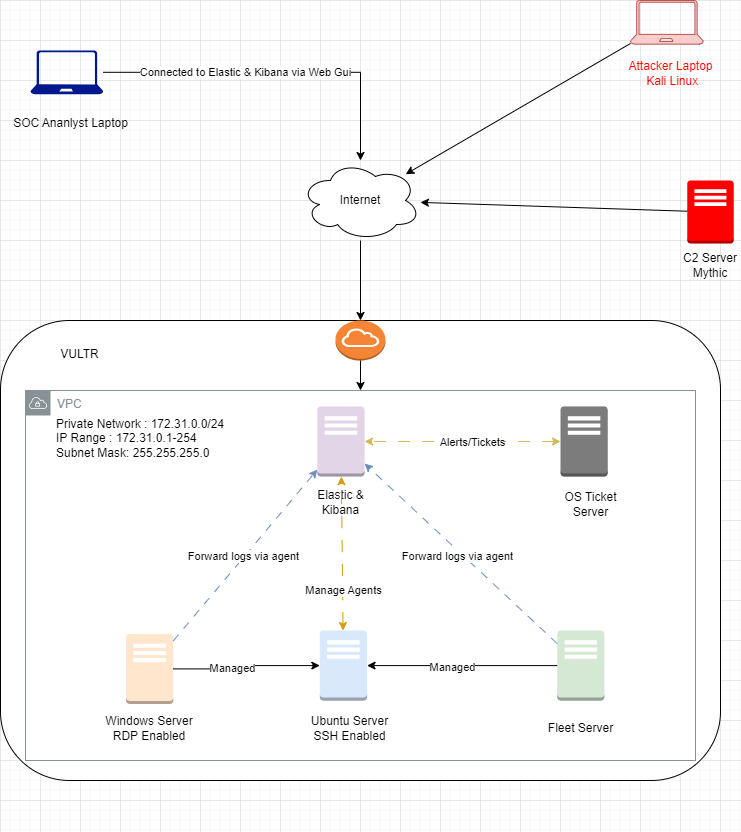
Day-1 Logical Diagram
Creating logical diagram
Importance of Logical Diagrams for SOC Analysts:
Logical diagrams provide a clear and concise visualization of network infrastructure, aiding SOC analysts in:
- Understanding network topology: Identifying critical assets, potential vulnerabilities, and attack vectors.
- Simulating security scenarios: Testing response plans and identifying areas for improvement.
- Communicating effectively: Explaining complex security concepts to stakeholders and team members.
- Troubleshooting incidents: Pinpointing the root cause of security breaches and implementing effective countermeasures.
Components in diagram:
- Windows Server with RDP Enabled: This is a Windows-based server that allows remote access via Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). RDP provides a graphical interface for users to connect to and control the server from a remote location.
- Fleet Server: While the exact definition of a “Fleet Server” can vary depending on the context, it often refers to a server that manages or controls a group of devices or systems, such as a fleet of vehicles or computers.
- Ubuntu Server SSH Enabled: This is a Linux-based server (specifically Ubuntu) that allows secure shell (SSH) access. SSH provides a secure way to connect to and control the server from a remote location, often used for administrative tasks.
- Elastic & Kibana: These are open-source tools used for data analytics and visualization. Elastic is a distributed search and analytics engine, while Kibana provides a web interface for visualizing and interacting with the data stored in Elastic.
- OS Ticket Server: This is a server that manages and tracks support tickets, often used in IT help desks or service departments. It provides a centralized system for tracking and resolving issues.
- C2 Server (Mythic): A C2 server (Command and Control) is a server used by attackers to communicate with and control compromised systems. Mythic is a specific C2 framework often used for malicious activities.
- VULTR: This is a cloud infrastructure provider that offers virtual servers, storage, and networking services. It allows users to create and manage virtual machines (VMs) on demand.
- VPC: A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a private network within a public cloud infrastructure. It provides a secure and isolated environment for running applications and services.
- Internet Gateway: This is a network component that connects a VPC to the public internet, allowing resources within the VPC to communicate with external networks.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.