Day-15 Remote Desktop Protocol Introduction
Remote Desktop Protocol: A Double-Edged Sword ⚔️
What is RDP?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a powerful tool that enables users to access and control a remote computer over a network connection. It’s widely used for tasks like remote administration, troubleshooting, and accessing files from anywhere.
Why is it used?
- Remote Access: RDP allows users to access their work computers from home, on the go, or from other locations.
- Troubleshooting: IT professionals use RDP to diagnose and resolve technical issues on remote machines.
- File Sharing: Users can share files and access data stored on remote computers.
How attackers abuse it?
Despite its many benefits, RDP can also be a security vulnerability. Attackers can exploit RDP to gain unauthorized access to systems and networks. Common attack methods include:
- Brute Force Attacks: Attackers try different password combinations to guess the correct credentials.
- Credential Stuffing: Attackers use stolen credentials from other data breaches to attempt logins.
- Malware Injection: Attackers can use RDP to deploy malware onto vulnerable systems.
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Attackers intercept RDP traffic to steal credentials or inject malicious code.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Attackers can flood RDP servers with traffic to make them unavailable.
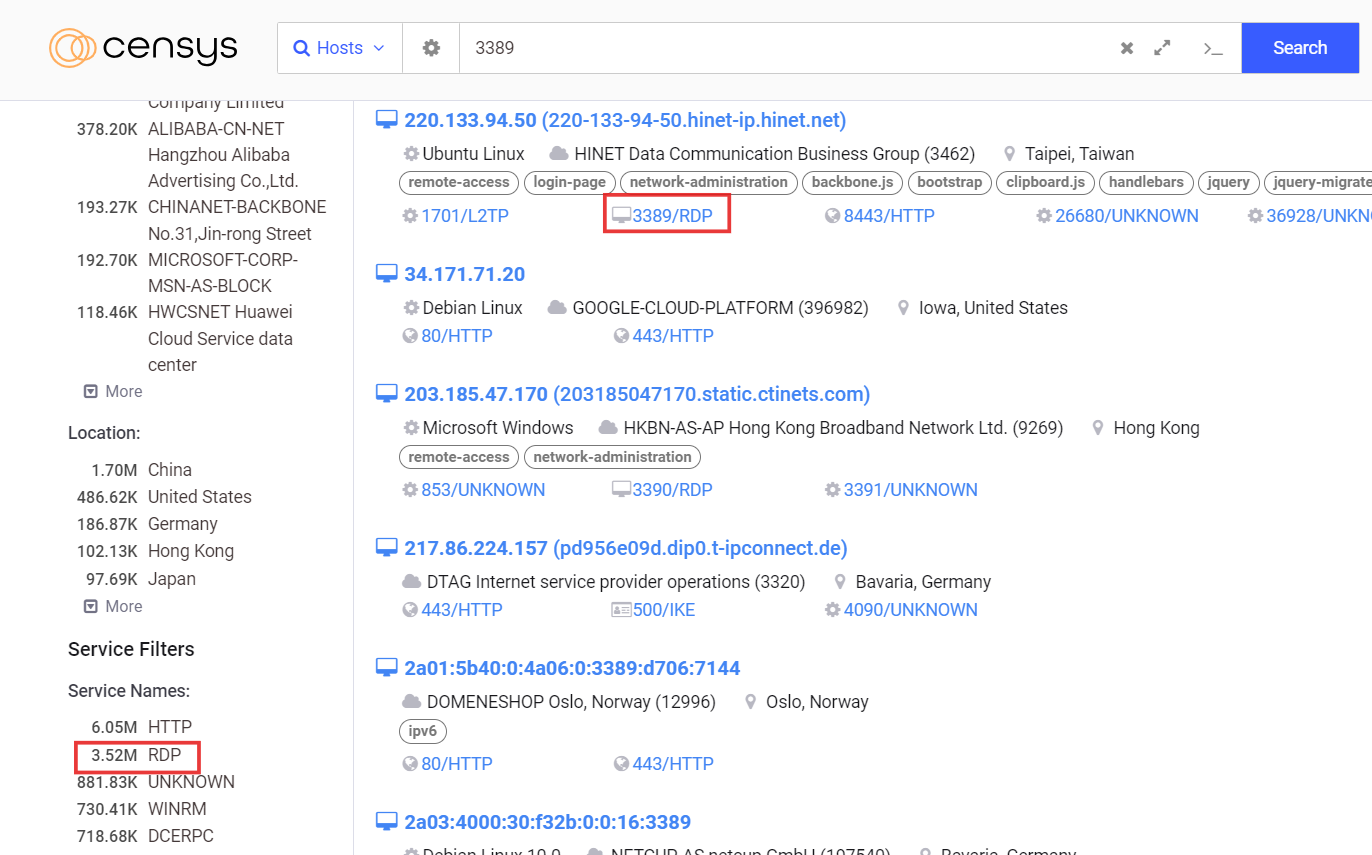
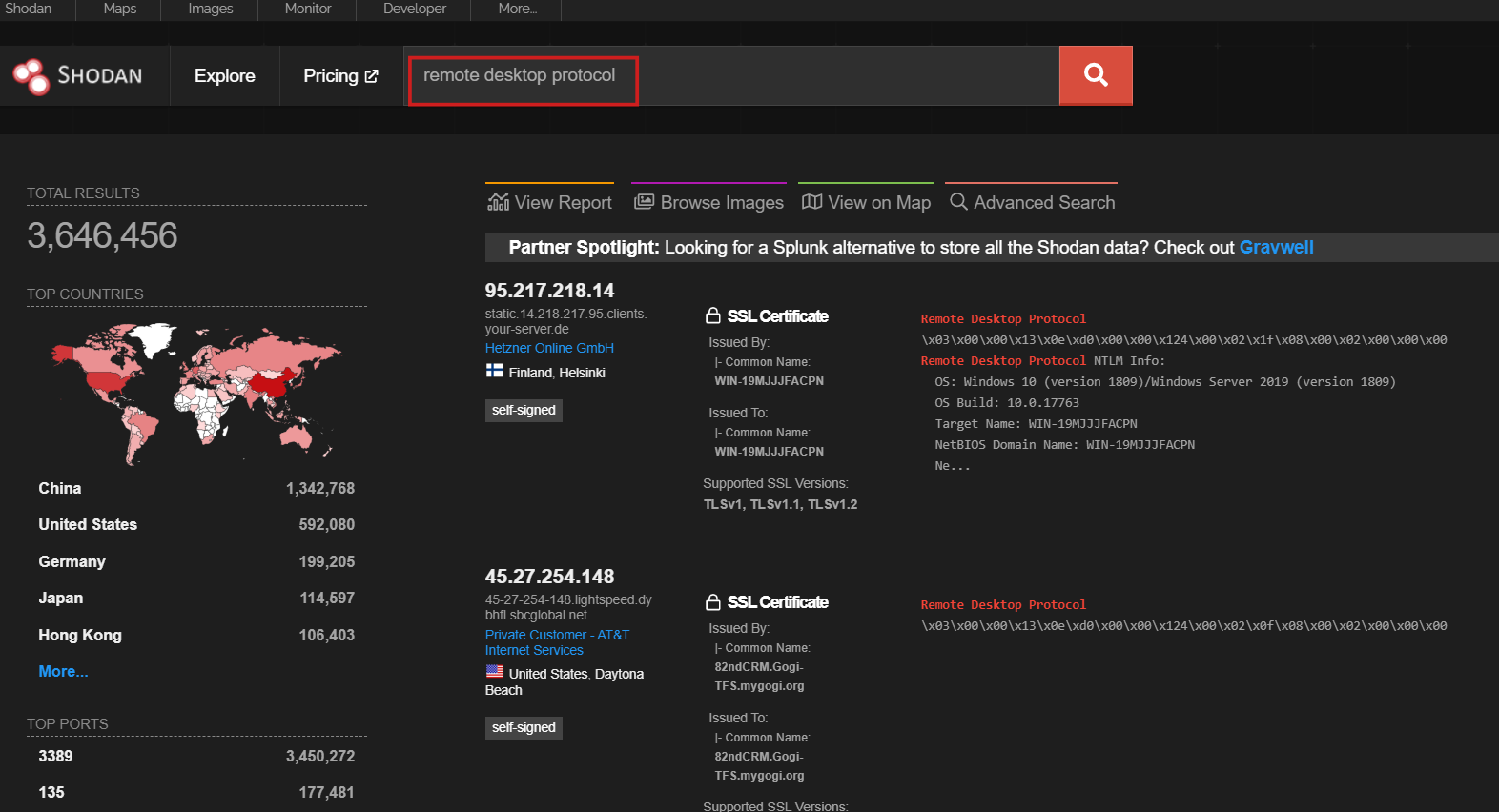
How to find endpoints with exposed RDP?
To identify endpoints with exposed RDP, you can use the following methods:
- Network Scanning: Use network scanning tools like Nmap or Nessus to detect open RDP ports (typically port 3389).
- Search Engines: Search for your organization’s domain name on search engines like Google or Bing to see if any exposed RDP instances are indexed.
Specialized Tools: Utilize tools like Shodan or Censys, which are specifically designed to search for exposed services on the internet.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: If your organization has a SIEM in place, it can help detect and alert you to any suspicious RDP activity.
How you can protect yourself?
To protect your RDP endpoints from attacks:
- Strong Passwords: Use complex, unique passwords for each RDP account.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implement 2FA to add an extra layer of security.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate RDP servers on a separate network segment to limit exposure.
- Regular Updates: Keep your operating system and RDP software up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Firewall Rules: Configure your firewall to restrict RDP access to authorized IP addresses.
- Monitoring and Logging: Monitor RDP activity and log all login attempts to detect suspicious behavior.
- Alternative Remote Access Solutions: Consider using more secure alternatives like VPNs or cloud-based remote desktop solutions.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate your users about the risks of RDP and how to protect themselves from attacks.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities in your RDP environment.
- Implement Security Best Practices: Follow industry-standard security best practices to reduce the risk of RDP-related attacks.
By following these best practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of RDP-related attacks and protect your systems from unauthorized access.
🔖Explore further: