Day-4 Kibana Setup
Alright, let’s move on to setting up Kibana on our Day 3 adventure! Here’s how we’ll access the Kibana interface using your server’s public IP:
1. Download and Install Kibana:
- Open your server instance on Vultr.
- Head over to the Kibana download page and copy the download link for the DEB package (similar to what we did for Elasticsearch).
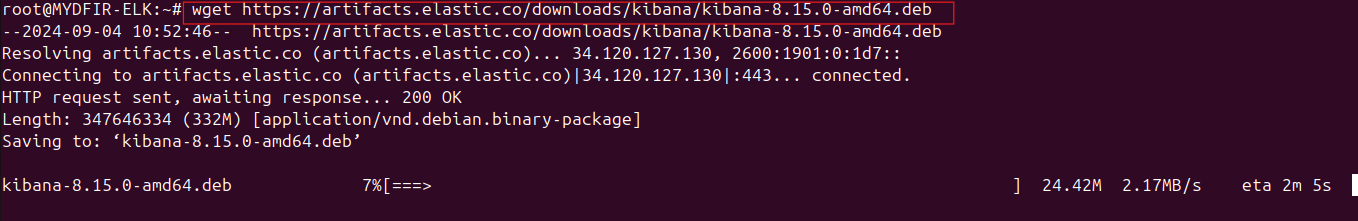
Download Kibana using the following command, replacing
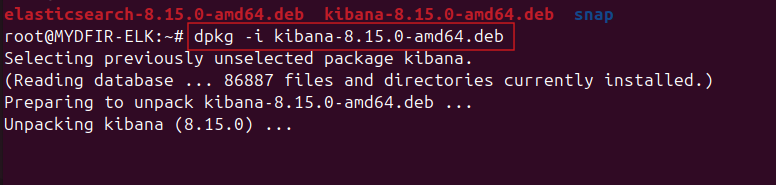
<kibana….deb>with the actual link:#wget <kibana….deb>Unpack the downloaded file:
#dpkg -i <kibana….deb>
2. Kibana Configuration:
Now, let’s edit the Kibana configuration file. Go to the directory containing the file and use nano to edit it:
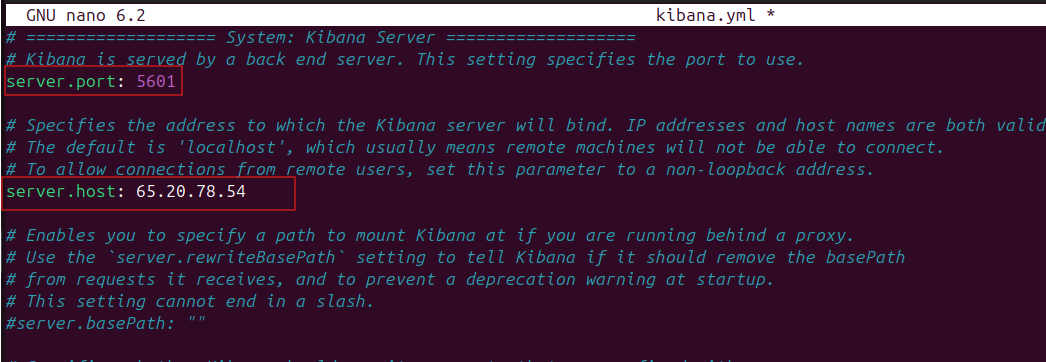
#cd /etc/kibana#nano kibana.yml- Look for the
server.hostsetting and edit it to match your server’s public IP address. - While you’re at it, uncomment both the
server.hostandserver.portsettings.
3. Start and Verify Kibana:
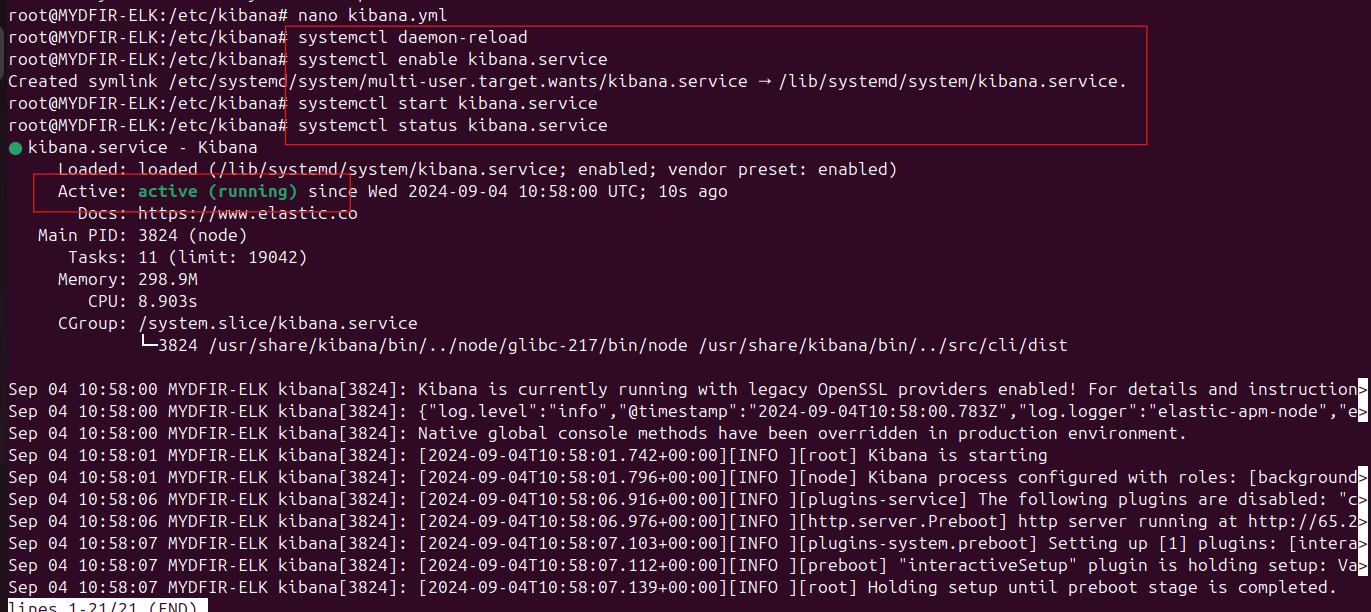
We need to reload the system daemon, enable the Kibana service at boot, and then start the service itself. Run these commands one by one:
#systemctl daemon-reload#systemctl enable kibana.service#systemctl start kibana.service#systemctl status kibana.serviceThe last command will show the status of the Kibana service. Verify that it’s running.
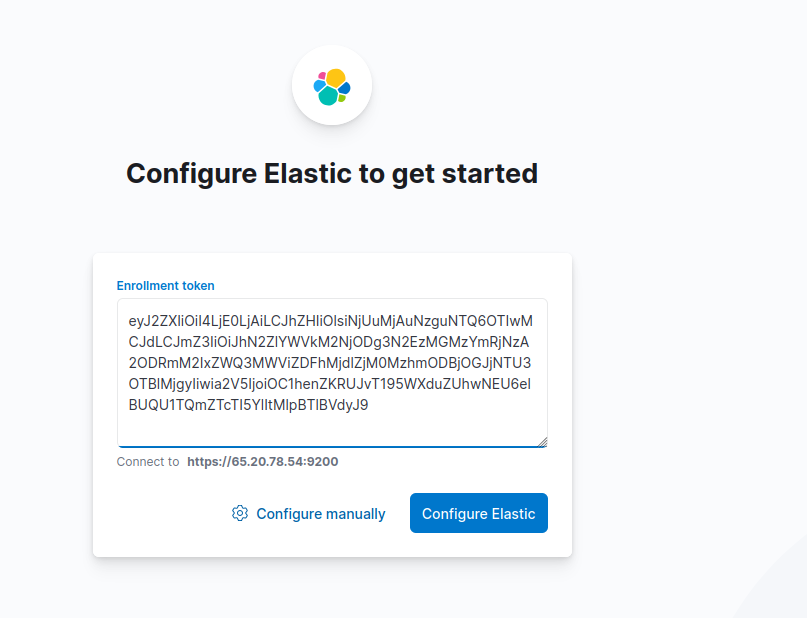
4. Generate Enrollment Token:
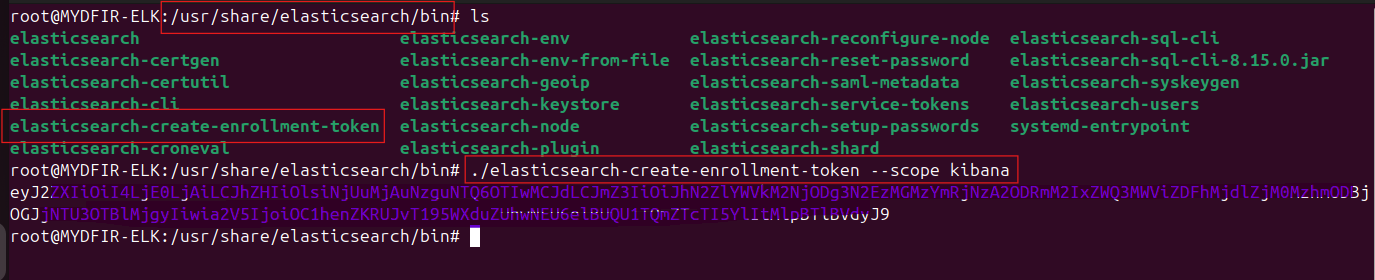
To access Kibana, we’ll need a special token. Let’s change directories first:
#cd /usr/share/elasticsearch/binNow, generate the token using the following command:
#./elasticsearch -create-enrollment-token --scope kibanaCopy the generated token.
5. Access Kibana Interface:
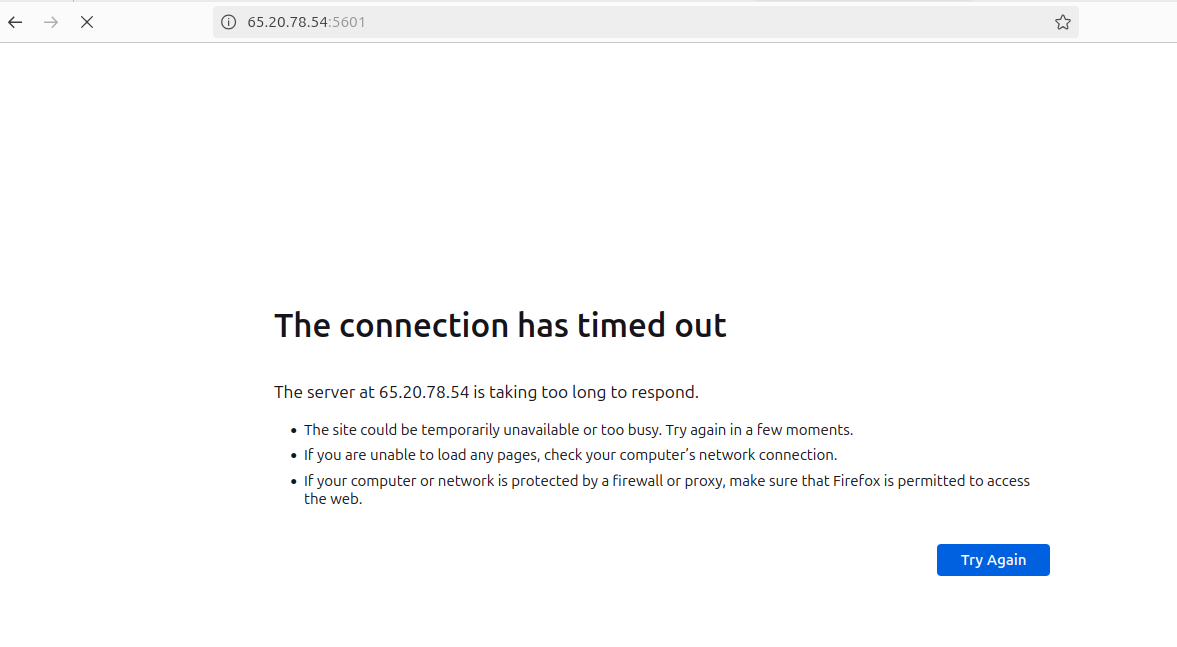
Open a web browser and navigate to your server’s public IP address, followed by the Kibana port number (usually 5601).
Troubleshooting:
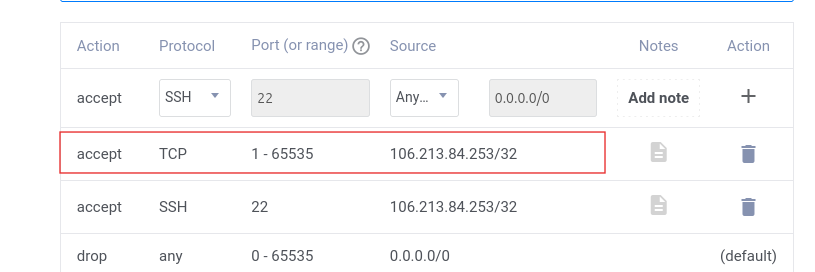
If you encounter a “site unreachable” or “timeout” error, you might need to adjust your firewall settings. Add a rule to allow access on port 5601 and restart the firewall service.
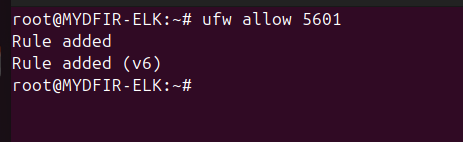
And if still it’s not working then you can use commands like
#ufw allow 5601for firewall management.Once you’ve addressed the firewall issue, refresh the page in your browser. Now, you should be able to see the Kibana interface.
6. Login to Kibana:
On the interface, you’ll be prompted to enter the enrollment token. Paste the token you copied earlier and click “Configure Elastic”.
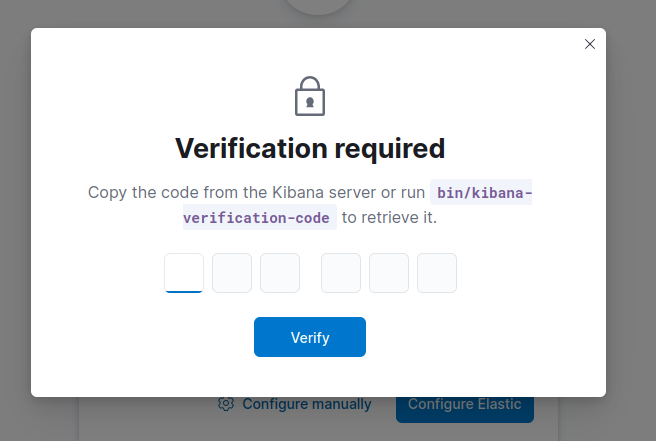
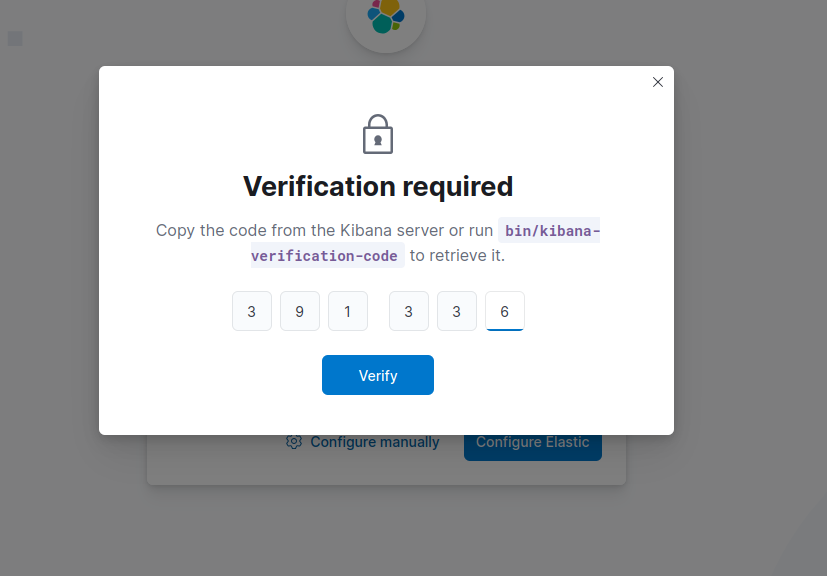
7. Verification Code:
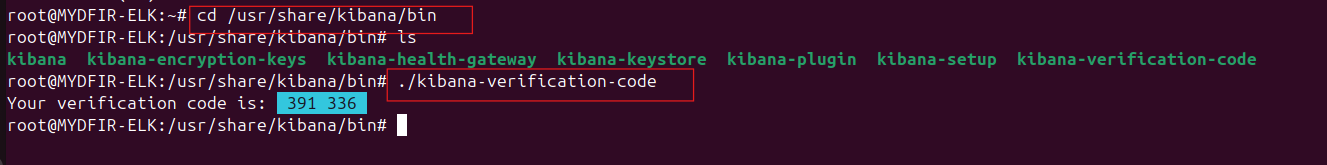
To get the verification code, navigate back to your server instance and run:
#cd /usr/share/kibana/bin#lsThis will list available commands#./kibana-verification-codeCopy the verification code displayed.
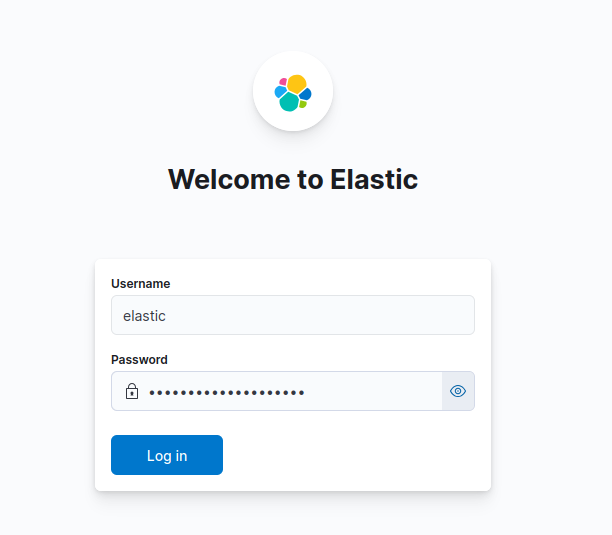
8. Enter Credentials:
Now, you should see a login prompt. Remember that security configuration screen you got earlier? Use the username and password listed there (usually username: “elastic” and password found in the configuration). Enter these credentials and log in.
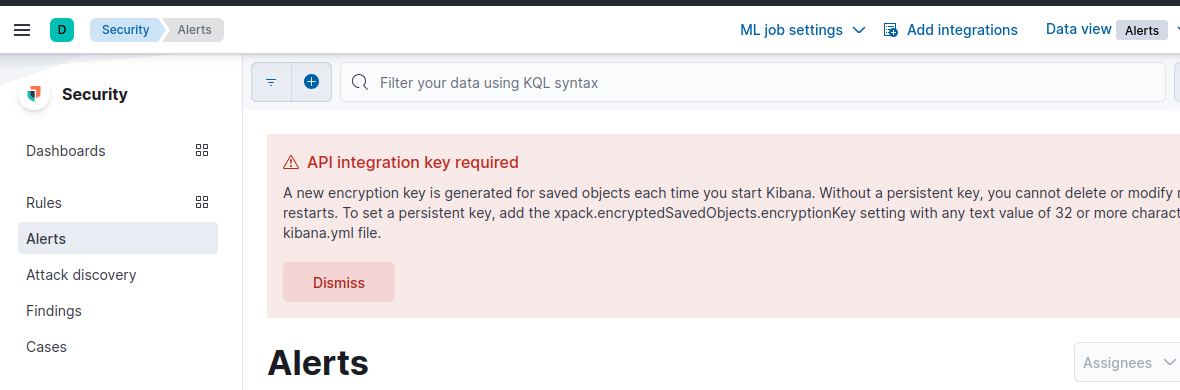
9. Encryption Keys:
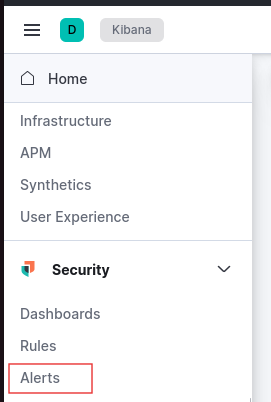
The last step involves adding encryption keys. Click on the hamburger menu (three horizontal lines) in Kibana, then navigate to Security > Alert. You’ll see an alert prompting you to add encryption keys.
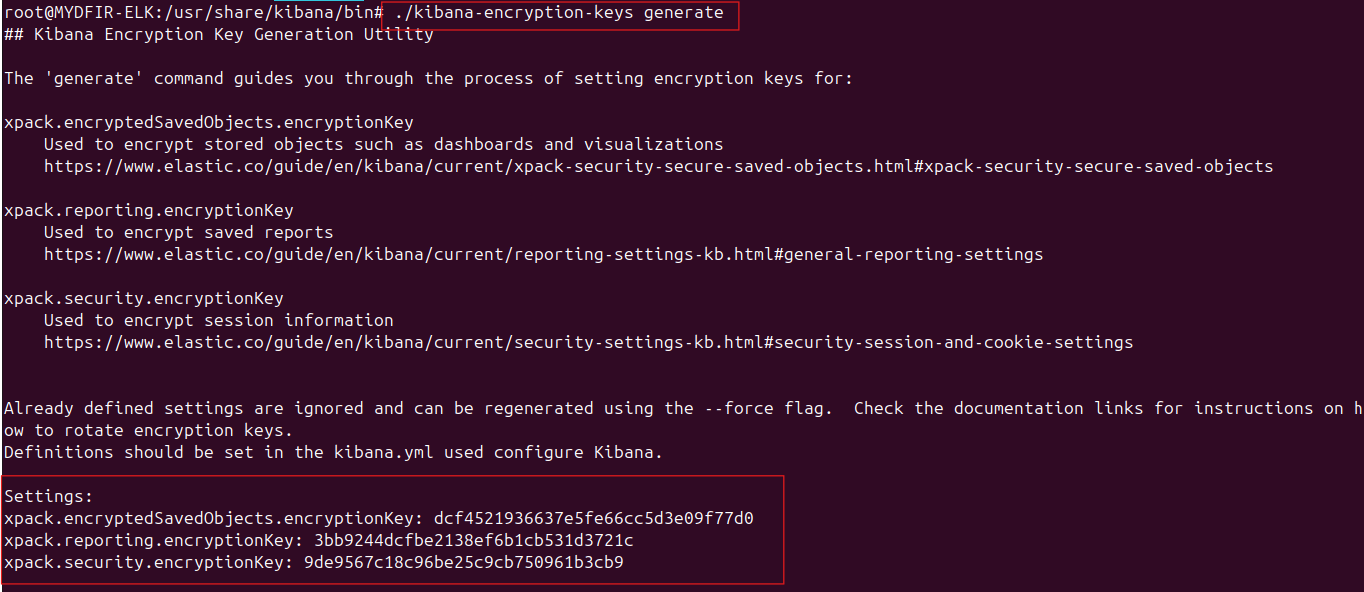
Back on your server instance, navigate to:
#cd /usr/share/kibana/bin#./kibana-encryption-keys generate- Copy the keys displayed in the “Settings” section and paste them into a notepad.
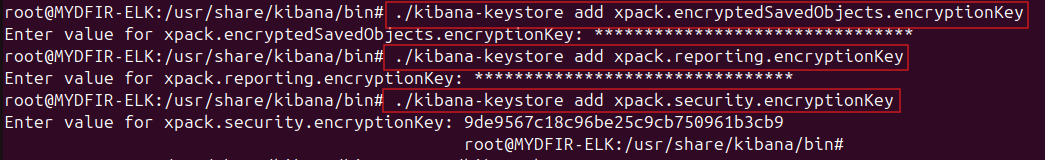
Use the following command (replacing
<name_of_the_key_without_colon>with the actual name) to add each key:#./kibana-keystore add <name_of_the_key_without_colon>- You’ll be prompted to enter a value; provide it, and repeat this two more times to add all three keys.
10. Restart and Enjoy!